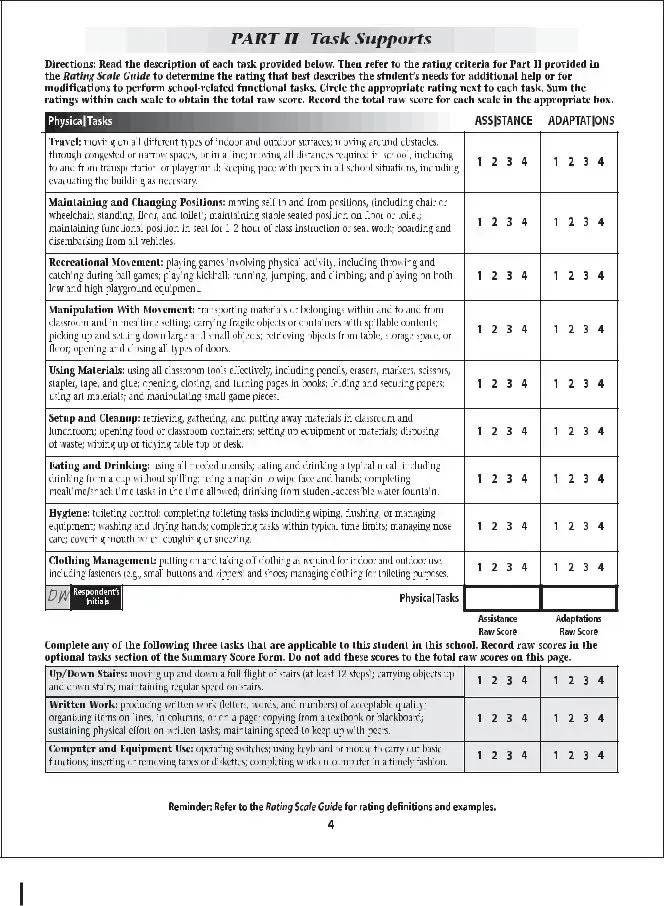
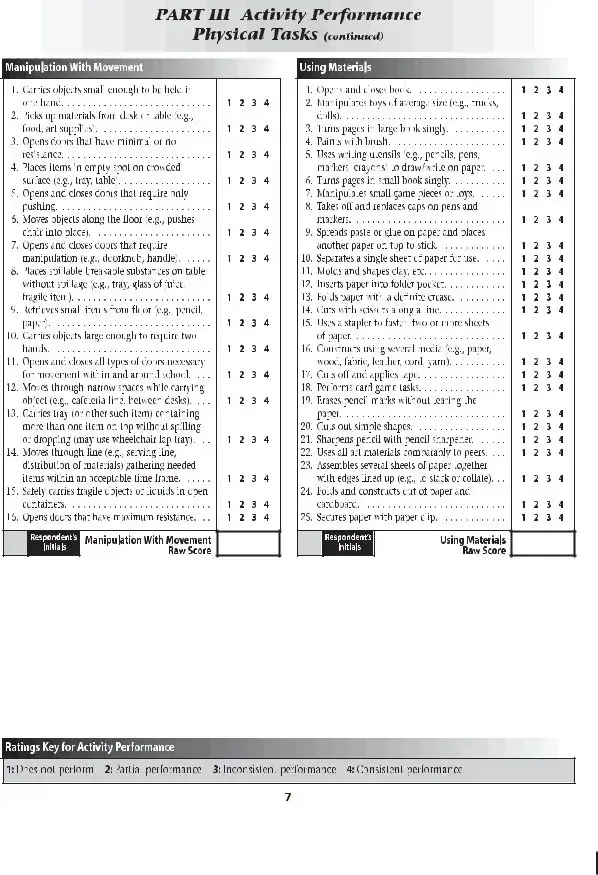
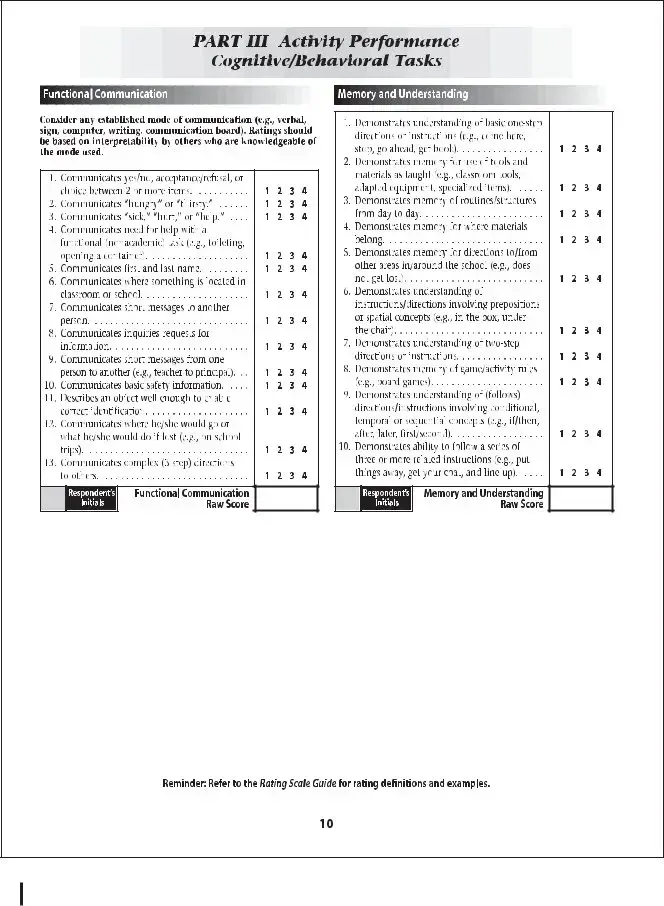
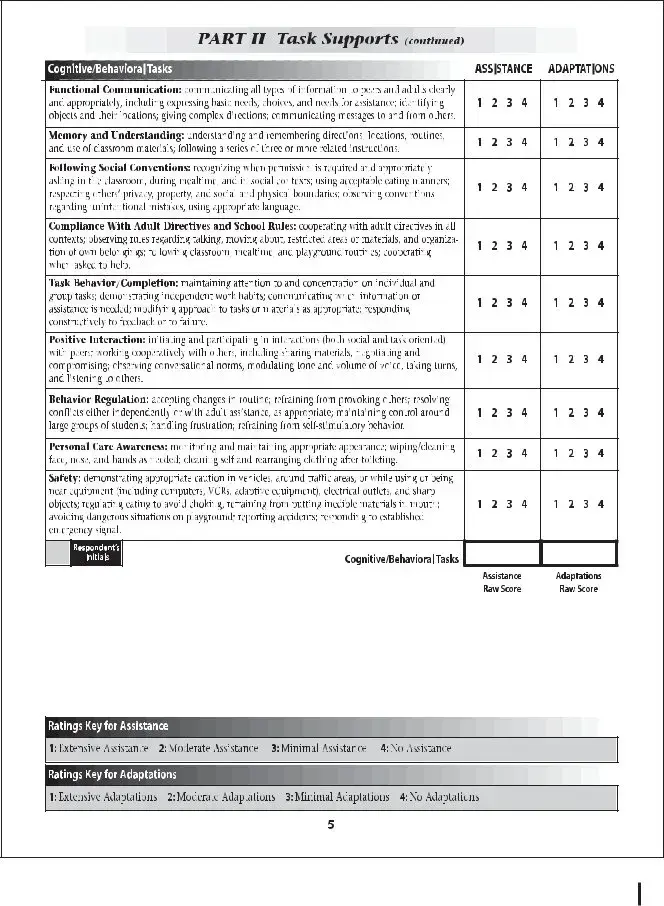
The Individual Education Plan (IEP) document closely aligns with the School Function Assessment form, as both are instrumental in evaluating and planning for a student's educational needs, especially for students with disabilities. The IEP provides a detailed and personalized program of instruction, including objectives, educational accommodations, and assessments tailored to the student, paralleling the School Function Assessment's focus on evaluating students' participation, support needs, and performance across various school activities.
Similarly, the 504 Plan document echoes the School Function Assessment in its purpose to provide supports and accommodations to students with disabilities, ensuring their access to education is on par with their non-disabled peers. While the 504 Plan does not necessarily entail academic or performance evaluation like the School Function Assessment, both aim at leveling the educational playing field for students facing challenges in regular education settings.
The Behavioral Intervention Plan (BIP) also shares common goals with the School Function Assessment. The BIP focuses on understanding a student's behavior in the school environment and creating strategies to improve or modify challenging behaviors. Like the School Function Assessment, it involves close observation and assessment to develop a tailored plan that addresses individual students' needs within the school context.
Student Accommodation Reports share a purpose with the School Function Assessment by identifying and implementing necessary accommodations that allow students to fully participate in their education. These reports analyze a student's abilities and challenges, much like the School Function Assessment, and propose interventions to augment their school experience and academic performance.
The Transition Plan, part of the IEP directed toward students 16 and older, bears similarities to the School Function Assessment in its focus on preparing students for post-secondary life. While the School Function Assessment may concentrate more on immediate function within school settings, both documents aim to equip students with the necessary skills and supports for future success, whether in further education, employment, or independent living.
Functional Behavior Assessments are used to understand the cause of certain behaviors in students and to formulate effective strategies to address them. This approach mirrors the School Function Assessment's goal of identifying and supporting students' needs within educational environments, focusing specifically on behavior as a key aspect of the student's overall school function.
Progress Reports, commonly used in all educational settings, complement the School Function Assessment by providing ongoing feedback on a student's academic and functional performance. While progress reports typically cover a broad range of subjects and skills, they serve a similar purpose of tracking and communicating students' development over time.
Occupational Therapy Evaluations in school settings examine students' physical abilities, like fine motor skills and general mobility, to participate effectively in school activities. These evaluations, similar to the School Function Assessment, aim to identify barriers to participation and learning, paving the way for targeted interventions.
Speech-Language Evaluations assess students' communication skills and are key to developing interventions that support language and speech development. Like the School Function Assessment, which may also consider communication as part of school functioning, these evaluations help in crafting strategies to improve students' participation and success in school settings.
The Gifted and Talented Student Assessment is designed to identify students who perform or show the potential for performing at remarkably high levels of accomplishment when compared to others of their age, experiences, or environment. While its focus differs from the School Function Assessment's emphasis on support and accommodation for students facing challenges, both types of assessments aim to tailor the educational experience to meet the unique needs of individual students, ensuring they are provided with the necessary resources to thrive academically.