Fill Out Your IRS Schedule B 941 Template
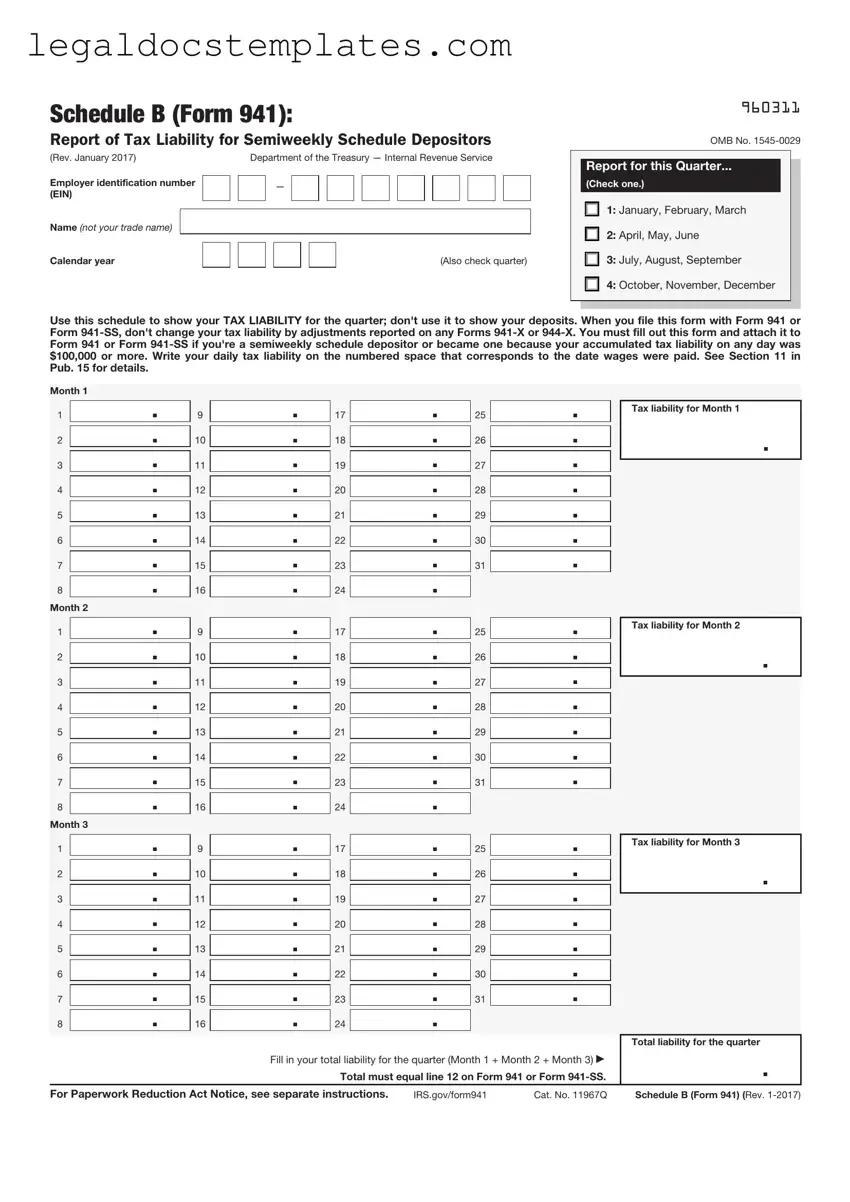
The IRS Schedule B 941 form is a tax document used by employers to report tax liability for semiweekly schedule depositors. It serves as a record of when payroll taxes were accrued, rather than when they were paid. For businesses that need to detail their tax liabilities for specific periods within a quarter, understanding and filling out this form correctly is crucial. Click the button below to begin filling out your form.
Access IRS Schedule B 941 Now
Fill Out Your IRS Schedule B 941 Template
Access IRS Schedule B 941 Now

Access IRS Schedule B 941 Now
or
⇩ PDF Form
Don’t spend hours on this form
Complete IRS Schedule B 941 online in minutes, fully digital.

 .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
.