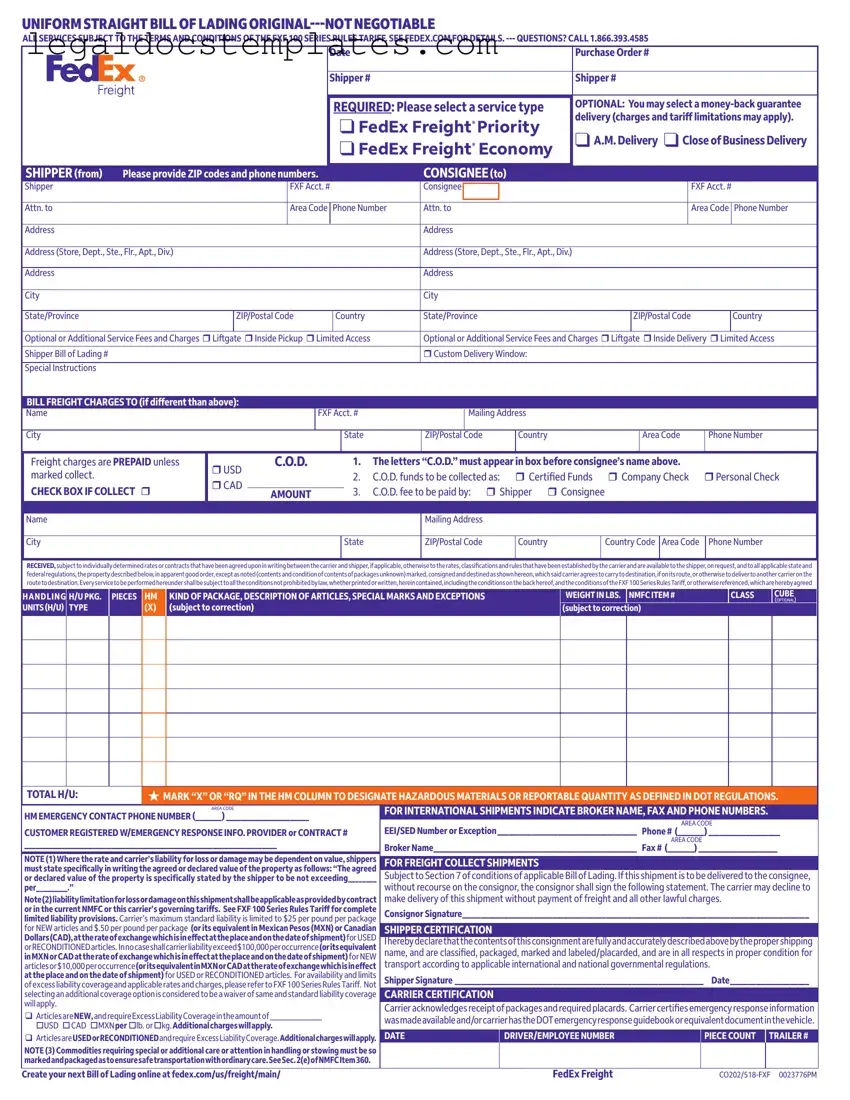
The Uniform Bill of Lading is a document that shares similarities with the FedEx Bill of Lading, used for detailing the contract for the shipment of goods. It acts as a receipt of freight services, a contract between a freight carrier and shipper and a document of title. The information it holds includes the nature, quantity, and destination of the goods being shipped. This helps ensure that all parties involved have a clear understanding of the terms of transportation.
The Commercial Invoice is another document related to the FedEx Bill of Lading. It provides information about the transaction between the seller and the buyer, specifying the goods sold, their price, and shipment details. While not a contract in the same sense, it plays a critical role in international shipments by serving as a declaration to customs authorities, helping determine the true value of imported goods for the assessment of duties and taxes.
The Shipper's Letter of Instruction (SLI) complements the FedEx Bill of Lading by providing additional details that assist in the shipping process. The SLI guides the carrier on how to handle, declare, and route a shipment, including instructions for export reporting and consignee details. Though not a legal document for the carriage of goods, it's crucial for ensuring compliance with export documentation requirements.
A Certificate of Origin is a document that certifies the country where the goods in a shipment were produced or manufactured. Its relevance to the FedEx Bill of Lading comes into play in international trade, where it may be required to determine whether certain goods are eligible for import, or whether they qualify for tariff exemptions or reductions under free trade agreements. Like the Bill of Lading, it is essential for customs clearance.
The Packing List is closely associated with the FedEx Bill of Lading, detailing the specific contents of each package within a shipment. This document helps carriers and customs officials verify the cargo, ensuring that the contents match what’s declared on the Bill of Lading and other shipping documents. It streamlines the process of checking and processing shipments for all stakeholders involved.
The Warehouse Receipt is similar to the FedEx Bill of Lading because it serves as proof that goods have been received for storage by a warehouse operator. Like the Bill of Lading, it outlines the goods’ description, quantity, and condition at the time of receipt. However, it pertains specifically to storage rather than the broader transport of goods from one location to another.
The Cargo Insurance Certificate provides details on the insurance coverage for the shipment of goods, complementing the FedEx Bill of Lading by offering proof of insurance protection against loss, damage, or theft during transport. While the Bill of Lading may limit the carrier's liability, the insurance certificate ensures the shipper can recover the value of the cargo if mishaps occur.
The Export Packing List offers more detailed information compared to the standard packing list, especially crucial for international shipments. It includes additional details about the weight and dimensions of packages, enhancing the data provided in the FedEx Bill of Lading. This document is vital for freight carriers and customs officials to assess cargo.
Away Bill is similar to the FedEx Bill of Lading but is typically used for air freight. It acts as a receipt of goods by an airline (the carrier), a contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier, and sometimes as a document for customs clearance. Like the Bill of Lading, it provides detailed information regarding the shipper, consignee, and the nature and quantity of goods being transported.
Lastly, the Delivery Order is issued based on the Bill of Lading. It authorizes the release of cargo to the consignee or a named party. This document is essential for the last part of the supply chain, where it instructs the carrier or warehousing company to release the goods to the rightful recipient, as indicated in the Bill of Lading.