Similar to the CNA Shower Sheets form, the Braden Scale for Predicting Pressure Sore Risk is a healthcare document used to assess a patient's risk of developing pressure ulcers. It involves a comprehensive evaluation of factors such as sensory perception, moisture, activity, mobility, nutrition, and friction/shear. Like the CNA Shower Sheets, the Braden Scale requires healthcare professionals to conduct a visual and physical examination of the patient's skin, but it also incorporates additional aspects of the patient's overall health and ability to respond to pressure-related injury.
The Falls Risk Assessment Tool is another document that bears resemblance to the CNA Shower Sheets. It is designed to identify patients at high risk of falling, incorporating various factors such as history of falls, medication use, mobility issues, and sensory deficits. While the focus is different, both documents serve a similar purpose in promoting patient safety through timely and proactive identification of risk factors. The CNA Shower Sheets form's emphasis on skin integrity can also play a role in falls prevention, as skin conditions may impact mobility and the risk of injuries from falls.
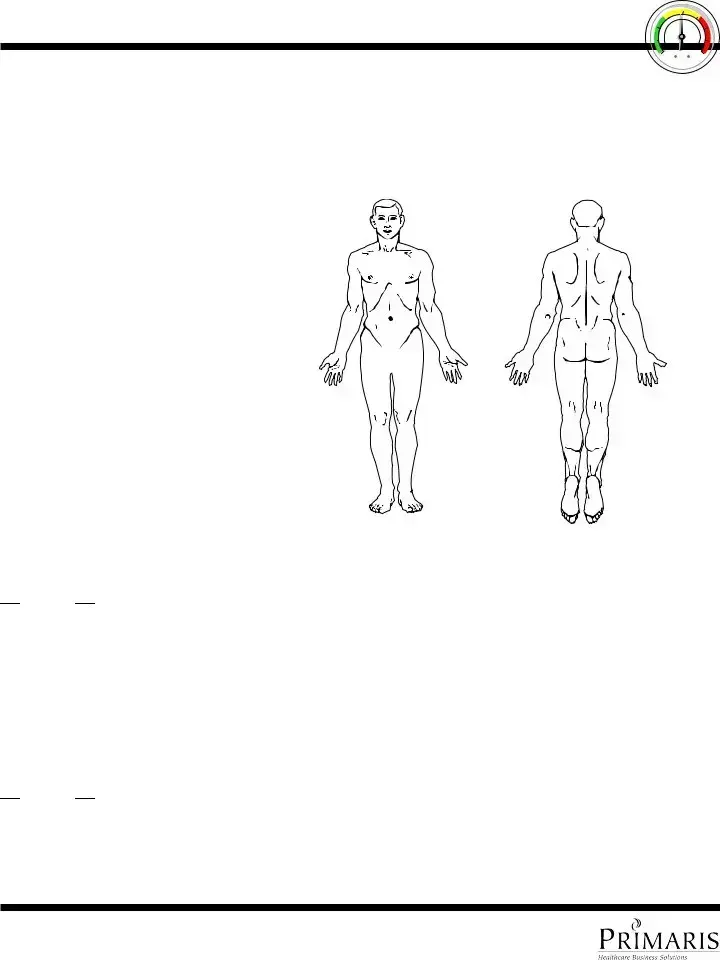
The Wound Assessment Form is closely related to the CNA Shower Sheets form in its focus on skin integrity but is more specialized towards the monitoring and documentation of wounds. This form includes detailed sections for recording the location, stage, size, and appearance of wounds, much like the CNA Shower Sheets require descriptions and charting of skin abnormalities. Both forms are integral in ensuring appropriate and timely medical intervention to prevent infection and promote healing.
The Nutrition Assessment Form, while not directly related to skin care, shares similarities with the CNA Shower Sheets in its approach to preventive care. It assesses a resident's nutritional status, identifying risks that could contribute to health issues, including poor skin health. Malnutrition can exacerbate skin problems, making nutrition assessments complementary to the skin monitoring conducted with the CNA Shower Sheets. Both forms are tools in the broader context of maintaining and improving patient health.
The Daily Nursing Assessment Form is a general document that encompasses a wide range of health indicators, including skin condition, which the CNA Shower Sheets focus on specifically. The daily assessment form is used by nurses or CNAs to document vital signs, mental status, mobility, and other health aspects that can indicate changes in a patient's condition. This holistic approach includes elements of the skin assessment performed with the CNA Shower Sheets, highlighting the interconnectedness of various health assessments.
Medication Administration Records (MAR) share a procedural similarity with the CNA Shower Sheets, as both involve regular, scheduled documentation critical to patient care. Though the MAR focuses on the administration of medications, tracking dosages, administration times, and reactions, it parallels the vigilant monitoring and reporting approach seen with skin assessments on the CNA Shower Sheets. Both are preventative in nature, aiming to avoid adverse outcomes through diligent observation and record-keeping.
The Falls Intervention Plan mirrors the preventative framework of the CNA Shower Sheets, albeit with a focus on fall prevention. This document outlines specific interventions tailored to reducing a patient's risk of falling. Similar to how skin abnormalities are noted and addressed through interventions on the CNA Shower Sheets, the Falls Intervention Plan uses the information gathered through assessments to implement strategies designed to protect patients from harm.
The Healthcare Incident Report, while not used routinely like the CNA Shower Sheets, is invoked following adverse events or near misses. It shares the objective of improving patient safety through documentation and communication. Incident reports and the CNA Shower Sheets both require detailed description of the events or findings, immediate actions taken, and follow-up measures to prevent recurrence. They serve as essential tools in quality improvement and risk management within healthcare settings.



 Yes
Yes 
 No
No
 Yes
Yes 
 No
No